Openx Cluster Handbook – 121 cluster Openx High performance simple cluster based on Nginx, lighttpd/apache
Index
Disclaimer :Please notices this document will help you for configuring an simple highperformance cluster for hosting Openx services. This article is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-No ncommercial 2.5 India .Please don’t copy and paste the configurations to your server if it is not the hardware that mentioned in the hardware requirements.
1. Introduction
This document help you to setup a simple cluster for starters. This configuration using the best and popular software configuration for getting better stability and performance. This can be used for Openx cluster platforms and large vbulletin forums. Please not this is not a high availability solution but cluster. You can build this cluster with a minimum of 4 servers.
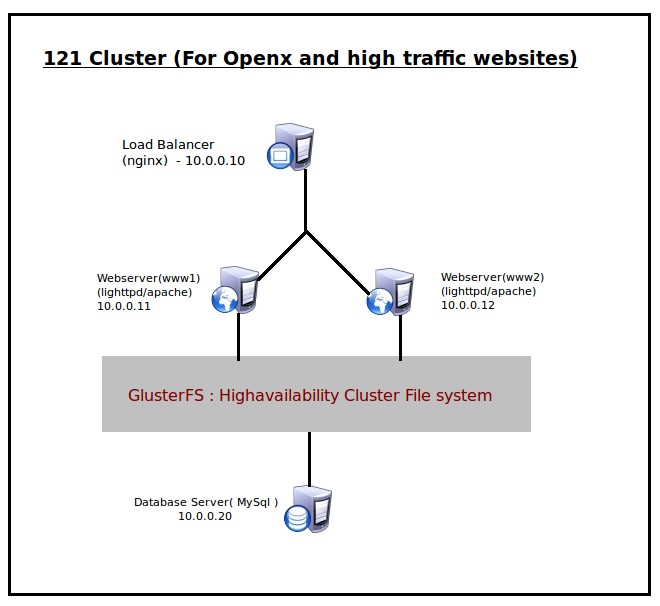
1.1 Why the name 121 Cluster?
Let me explain 1-2-1 cluster means ,
- 1 – Load balancer
- 2 – Werbserver , or multiple of 2
- 1 – Database server
So this configuration is based on one load balancer , two or multiple of 2′s of webservers and one database server. Here all are servers there is no need to buy external devices. This is the simplest and well optimized cluster that you can build. You can see a graphical representation of this cluster as below,
1.2 Technology
We are here using Nginx webserver as http load balanced Proxy. It is the most popular proxy application and around 6% of high traffic websites in this world usin nginx. Some example sites using nginx are wordpress.com ,rambler.ru,fastmail.fm
Behind these proxies we use lighttpd as webservers for hosting our application. Lighttpd is a fast webserver with light foot print. It can simply handle millions of requests without increasing server load.It is designed and optimized for high performance environments. With a small memory footprint compared to other web-servers, effective management of the cpu-load, and advanced feature set (FastCGI, SCGI, Auth, Output-Compression, URL-Rewriting and many more) lighttpd is the perfect solution for every server that is suffering load problems.
2. System Requirements
Here we using the best webservers and proxy applications available on industry. It is fully a service based cluster. So no worry about kernel panics and OS corruptions. Also if you have a private LAN across these nodes, it is good to configure it otherwise you need to proxify the access over internet.
2.1 Load Balancer Node
This node is your public node,, That means your Openx/website domain is pointing to this server IP. I recommend to install ubuntu server Operating system/ Centos for your load balanced server. Here in this article I am mentioning the procedure based on ubuntu.
2.2 Web Servers Node
You may need a minimum of two webservers or multiple of 2, beacuse I am configuring GlusterFS between these webservers for file sharing. GlusterFS is one of the top cluster file system which is built on ext3. With 4 webservers you can configure a RAID10 like GlusterFs file system. That mean your cluster will work if 50% of node go down. It have automatic mirroring and scaling capacity. So there is no need to sync your website / openx contents regularly.
You can chose centos/ubuntu Os as operating system in webserver nodes. If you going to install cPanel then you can only use apache as webservers. Also remember the webservers must need same type of hardware configurations.
2.3 Database Server Node
As it is a single cluster we only use one database sever for Mysql. I recommend to use a bigger configuration of for this server as follows,
- Processor -Dual Quad core AMD/ Xeon
- RAM – 12 GB
- HDD – SAS RAID 10
Again Use Centos as operating system in this server
3. Install and Configure Load Balancer
Please see the picture , the top one is load balance. Let us use the same IP as in this example. Download the latest stable version of Nginx from here .I used nginx-0.7.62.tar.gz . Please proceed as follows.
# wget -c http://sysoev.ru/nginx/nginx-0.7.62.tar.gz # tar -xzf nginx-0.7.62.tar.gz # cd nginx-0.7.62/ # ./configure --prefix=/opt/nginx # make # make install
Please resolve the dependencies before make.Now we installed Nginx here. It is a best webserver eventhough we can use it as load balanced proxy. The Nginx configuration file is /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf . Add the following contents to /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user nobody;
worker_processes 5;
error_log logs/error.log;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 4096;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
upstream my_openx_site {
server 10.0.0.11:80 weight=5; # this is your webserver www1
server 10.0.0.12:80 weight=5; # this is your web server www2
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://my_openx_site;
}
}
}
The above configuration have 5 worker processor and can handle 4096 requests per second. If you need more connections increase the limits.
Now add a user and group
# useradd nobody # groupadd nobody
Now give suitable permission for log folders.
# chown -R nobody.nobody /opt/nginx/logs/
Now we need to create a startup script. I have done some modification for the initscript as follows. Remember this is for ubuntu. Please copy the following contents to /etc/init.d/nginx
#! /bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: nginx
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: nginx init.d script for Ubuntu 8.10 and lesser versions.
# Description: nginx init.d script for Ubuntu 8.10 and lesser versions.
### END INIT INFO
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# nginx - this script, which starts and stops the nginx daemon for ubuntu.
#
# description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \
# proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server. This \
# script will manage the initiation of the \
# server and its process state.
#
# processname: nginx
# config: /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
# pidfile: /opt/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
# Provides: nginx
#
# Notes: nginx init.d script for Ubuntu 8.10 and lesser versions.
Functions
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Consts
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
DAEMON=/opt/nginx/sbin/nginx
NAME=nginx
DESCRIPTION="Nginx Server..."
PIDSPATH=/opt/nginx/logs
PS=$NAME #the process, which happens to be the NAME
PIDFILE=$NAME.pid #pid file
RUNAS=root #user to run as
SCRIPT_OK=0 #ala error codes
SCRIPT_ERROR=1 #ala error codes
TRUE=1 #boolean
FALSE=0 #boolean
lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf"
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Simple Tests
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#test if nginx is a file and executable
test -x $DAEMON || exit 0
# Include nginx defaults if available
if [ -f /etc/default/nginx ] ; then
. /etc/default/nginx
fi
#set exit condition
#set -e
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Functions
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
configtest() {
$DAEMON -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
getPSCount() {
return `pgrep -f $PS | wc -l`
}
isRunning(){
pidof_daemon
PID=$?
if [ $PID -gt 0 ]; then
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
status(){
isRunning
isAlive=$?
if [ "${isAlive}" -eq $TRUE ]; then
echo "$NAME found running with processes: `pidof $PS`"
else
echo "$NAME is NOT running."
fi
}
removePIDFile(){
if [ -f $PIDSPATH/$NAME.pid ]; then
rm $PIDSPATH/$NAME.pid
fi
}
start() {
log_daemon_msg "Starting $DESCRIPTION"
isRunning
isAlive=$?
if [ "${isAlive}" -eq $TRUE ]; then
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_ERROR
else
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --chuid $RUNAS --pidfile $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE --exec $DAEMON
chmod 400 $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_OK
fi
}
stop() {
log_daemon_msg "Stopping $DESCRIPTION"
isRunning
isAlive=$?
if [ "${isAlive}" -eq $TRUE ]; then
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --pidfile $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE
removePIDFile
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_OK
else
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_ERROR
fi
}
reload() {
configtest || return $?
log_daemon_msg "Reloading (via HUP) $DESCRIPTION"
isRunning
if [ $? -eq $TRUE ]; then
`killall -HUP $PS` #to be safe
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_OK
else
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_ERROR
fi
}
terminate() {
log_daemon_msg "Force terminating (via KILL) $DESCRIPTION"
PIDS=`pidof $PS` || true
[ -e $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE ] && PIDS2=`cat $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE`
for i in $PIDS; do
if [ "$i" = "$PIDS2" ]; then
kill $i
removePIDFile
fi
done
log_end_msg $SCRIPT_OK
}
pidof_daemon() {
PIDS=`pidof $PS` || true
[ -e $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE ] && PIDS2=`cat $PIDSPATH/$PIDFILE`
for i in $PIDS; do
if [ "$i" = "$PIDS2" ]; then
return 1
fi
done
return 0
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart|force-reload)
stop
start
;;
reload)
$1
;;
status)
status
;;
configtest)
$1
;;
terminate)
$1
;;
*)
FULLPATH=/etc/init.d/$NAME
echo "Usage: $FULLPATH {start|stop|restart|force-reload|status|configtest|terminate}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
Now give execute permission to this script
# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/nginx
This is all about Load balancer configuration. You can start the Load balance, before that you may need to build your webservers as described below,
4. Install and Configure Webserver
Now we need to configure our web servers. All request came to Load balancer will be passed to your webserver. You can use lighttpd or apache2.2.x as webserver . I recommend to you lighttpd as webserver , because it can handle very high traffic websites with zero load. Before that we are going to configure gluster fs file system among the webserver. These file system is very scalable and high available.
4.1 File system configuration
If you don’t need a common file system, please skip this step.Let us use the minimal number of webservers for Glusterfs. If you have 4 webservers, it is easy to setup a RAID10 model cluster file system. Here we use two servers.
Download the latest stable version of glusterfs from http://www.gluster.com/ . I here used version glusterfs-2.0.2
# tar -xzf glusterfs-2.0.2.tar.gz # cd glusterfs-2.0.2/ # ./configure # make # make install
Now create the configuration files as follows.
# mkdir /etc/glusterfs/ # touch /etc/glusterfs/glusterfsd.vol
The server itself can act as server and client . The GFS server configuration is /etc/glusterfs/glusterfsd.vol . Now add the following contents to this file.
# file: /etc/glusterfs/glusterfsd.vol volume posix type storage/posix option directory /data # this partition is sharing end-volume volume locks type features/locks subvolumes posix end-volume volume brick type performance/io-threads option thread-count 8 subvolumes locks end-volume volume server type protocol/server option transport-type tcp option auth.addr.brick.allow * subvolumes brick end-volume
Now create the GlusterFS client configuration file /etc/glusterfs/glusterfs-client.vol as follows
# file /etc/glusterfs/glusterfs-client.vol volume remote1 type protocol/client option transport-type tcp option remote-host 10.0.0.11 option remote-subvolume brick end-volume volume remote2 type protocol/client option transport-type tcp option remote-host 10.0.0.12 option remote-subvolume brick end-volume volume distribute type cluster/distribute subvolumes remote1 remote2 end-volume volume writebehind type performance/write-behind option window-size 1MB subvolumes distribute end-volume volume cache type performance/io-cache option cache-size 512MB subvolumes writebehind end-volum
So now we have both client and server configuration for the Glusterfs file system. Here the /data partition is sharing around the webservers. You may need to create same configuration in all webservers.
Now start the glusterfs server
# /etc/init.d/glusterfsd start
Now mount the file system to /home as follows
# glusterfs -f /etc/glusterfs/glusterfs-client.vol /home
Add the above line to rc.local file so during reboot your file system will mount automatically. So now we have a common files system among the webserver nodes.
4.2 Lighttpd installation
Please note either you install lighttpd as webserver or use apache. If you going to chose apache please jump to next step.
Download the lighty from http://www.lighttpd.net/download I used the latest version.
# wget -c http://www.lighttpd.net/download/lighttpd-1.4.23.tar.gz # tar -xzf lighttpd-1.4.23.tar.gz # cd lighttpd-1.4.23/ # ./configure --prefix=/opt/lighttpd --enable-fastcgi --with-openssl # make # make install # mkdir -p /etc/lighttpd/ # cp doc/lighttpd.conf /etc/lighttpd/ # cp doc/rc.lighttpd.redhat /etc/init.d/lighttpd # chmod 755 /etc/init.d/lighttpd
Now edit the init script /etc/init.d/lighttpd and update the following line as given below,
lighttpd="/opt/lighttpd/sbin/lighttpd"
ow we need to configure lighttpd with php. Please install php as fcgi module. It is easy
Download the latest stable php from http://php.net/ and extract it. Now build it as follows,
# /configure --prefix=/usr/local/php5/ \ --with-config-file-path=/usr/local/php5/etc \ --enable-force-cgi-redirect --enable-fastcgi\ --with-gd --with-jpeg-dir=/usr/local --with-zlib \ --with-openssl --with-mysql # make # make install # cp php.ini-dist /usr/local/php5/etc/php.ini
Now edit /etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf as follows.
server.modules = (
"mod_access",
"mod_fastcgi",
"mod_proxy",
"mod_scgi",
"mod_simple_vhost",
"mod_evhost",
"mod_accesslog" )
server.document-root = "/home/openx/public_html"
server.errorlog = "/var/log/lighttpd/error.log"
index-file.names = ( "index.php", "index.html",
"index.htm", "default.htm" )
mimetype.assign = (
".pdf" => "application/pdf",
".sig" => "application/pgp-signature",
".spl" => "application/futuresplash",
".class" => "application/octet-stream",
".ps" => "application/postscript",
".torrent" => "application/x-bittorrent",
".dvi" => "application/x-dvi",
".gz" => "application/x-gzip",
".pac" => "application/x-ns-proxy-autoconfig",
".swf" => "application/x-shockwave-flash",
".tar.gz" => "application/x-tgz",
".tgz" => "application/x-tgz",
".tar" => "application/x-tar",
".zip" => "application/zip",
".mp3" => "audio/mpeg",
".m3u" => "audio/x-mpegurl",
".wma" => "audio/x-ms-wma",
".wax" => "audio/x-ms-wax",
".ogg" => "application/ogg",
".wav" => "audio/x-wav",
".gif" => "image/gif",
".jar" => "application/x-java-archive",
".jpg" => "image/jpeg",
".jpeg" => "image/jpeg",
".png" => "image/png",
".xbm" => "image/x-xbitmap",
".xpm" => "image/x-xpixmap",
".xwd" => "image/x-xwindowdump",
".css" => "text/css",
".html" => "text/html",
".htm" => "text/html",
".js" => "text/javascript",
".asc" => "text/plain",
".c" => "text/plain",
".cpp" => "text/plain",
".log" => "text/plain",
".conf" => "text/plain",
".text" => "text/plain",
".txt" => "text/plain",
".dtd" => "text/xml",
".xml" => "text/xml",
".mpeg" => "video/mpeg",
".mpg" => "video/mpeg",
".mov" => "video/quicktime",
".qt" => "video/quicktime",
".avi" => "video/x-msvideo",
".asf" => "video/x-ms-asf",
".asx" => "video/x-ms-asf",
".wmv" => "video/x-ms-wmv",
".bz2" => "application/x-bzip",
".tbz" => "application/x-bzip-compressed-tar",
".tar.bz2" => "application/x-bzip-compressed-tar",
"" => "application/octet-stream",
)
accesslog.filename = "/var/log/lighttpd/access.log"
url.access-deny = ( "~", ".inc" )
$HTTP["url"] =~ "\.pdf$" {
server.range-requests = "disable"
}
static-file.exclude-extensions = ( ".php", ".pl", ".fcgi" )
fastcgi.server = ( ".php" => ((
"bin-path" => "/usr/local/php5/bin/php",
"socket" => "/tmp/php.socket",
"max-procs" => 2,
"bin-environment" => (
"PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN" => "16",
"PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS" => "10000"
),
"bin-copy-environment" => (
"PATH", "SHELL", "USER"
),
"broken-scriptfilename" => "enable"
)))
So the above configuration will handle 10000 requests per children per second. You can adjust the factcgi.server options as you wish. Remember it is good all your webservers have same type configuration.
4.3 Apache installation
if you have cpanel or you are going to use apache2.2.x as webserver, please read my previous article to know how to configure it. Openx Hand Book
5. Install and Configure Database Server
Now you can install your mysql server and configure it.
# yum install mysql-server -y
Edit the my.cnf as follows(Remember it depend on your hardware )
[mysqld] safe-show-database old-passwords = 1 max_connections =2048 max_user_connections = 1024 key_buffer_size = 2048M myisam_sort_buffer_size = 64M join_buffer_size = 1M read_buffer_size = 1M sort_buffer_size = 2M table_cache = 4000 thread_cache_size = 384 wait_timeout = 20 connect_timeout = 10 tmp_table_size = 2048M max_heap_table_size = 512M max_allowed_packet = 64M net_buffer_length = 16384 max_connect_errors = 10 thread_concurrency = 16 concurrent_insert = 2 table_lock_wait_timeout = 30 read_rnd_buffer_size = 786432 bulk_insert_buffer_size = 8M query_cache_limit = 7M query_cache_size = 64M query_cache_type = 1 query_prealloc_size = 262144 query_alloc_block_size = 65536 transaction_alloc_block_size = 8192 transaction_prealloc_size = 4096 max_write_lock_count = 16 long_query_time = 5 skip-name-resolve skip-locking [mysqld_safe] open_files_limit = 8192 [mysqldump] quick max_allowed_packet = 16M [myisamchk] key_buffer = 384M sort_buffer = 384M read_buffer = 256M write_buffer = 256M
Now restart mysql server and create a database as follows
# mysqladmin create openx_db
Now go to mysql command prompt and create a user and password as follows
#mysql>grant all privileges on openx_db.* to 'openx_user'@'%' identified by 'VERYSTRONGPASSWORD';
So now for your openx configuration use host as your mysql serve IP(here 10.0.0.20) and database user and password same as above.
6. Optimization
Now it is time to optimize your servers.